Kidney Stones vs UTI: Expert Insights on Symptoms, Analysis, and Monitoring
Kidney Stones vs UTI: Expert Insights on Symptoms, Analysis, and Monitoring
Blog Article
An In-Depth Analysis of Therapy Choices for Kidney Stones Versus Urinary System System Infections: What You Required to Know
The difference in between therapy alternatives for kidney stones and urinary system system infections (UTIs) is essential for effective client monitoring. While UTIs are usually attended to with prescription antibiotics that offer fast alleviation, the approach to kidney stones can differ substantially based on specific variables such as stone size and make-up. Non-invasive approaches like extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL) might be suitable for smaller sized stones, yet bigger or obstructive stones frequently need even more intrusive techniques. Recognizing these nuances not just educates scientific choices yet likewise enhances client outcomes, welcoming a better evaluation of each problem's treatment landscape.
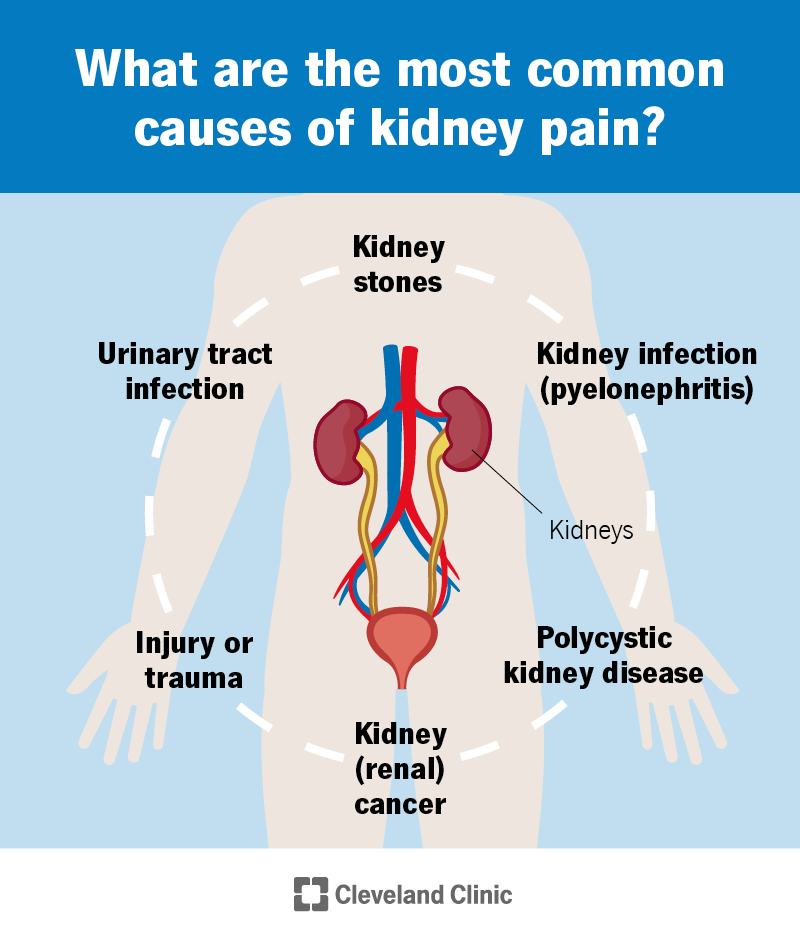
Recognizing Kidney stones
Kidney stones are difficult deposits created in the kidneys from minerals and salts, and recognizing their structure and development is vital for reliable administration. The key sorts of kidney stones include calcium oxalate, calcium phosphate, struvite, uric acid, and cystine stones, each with distinct biochemical origins. Calcium oxalate stones are one of the most common, normally resulting from high levels of calcium and oxalate in the urine. Factors such as dehydration, dietary habits, and metabolic disorders can add to their formation.
The development of kidney stones takes place when the focus of specific substances in the pee increases, leading to formation. This condensation can be affected by urinary pH, volume, and the existence of preventions or promoters of stone development. Reduced urine volume and high level of acidity are helpful to uric acid stone advancement.
Understanding these factors is vital for both avoidance and treatment (Kidney Stones vs UTI). Efficient administration techniques might consist of dietary modifications, increased fluid consumption, and, sometimes, pharmacological treatments. By recognizing the underlying reasons and kinds of kidney stones, medical care companies can execute tailored techniques to minimize recurrence and boost person outcomes
Review of Urinary Tract Infections
Urinary tract infections (UTIs) prevail microbial infections that can influence any kind of part of the urinary system, including the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. The bulk of UTIs are brought on by Escherichia coli (E. coli), a kind of germs normally located in the intestines. Women are more at risk to UTIs than males because of anatomical distinctions, with a much shorter urethra assisting in much easier microbial accessibility to the bladder.
Signs of UTIs can differ relying on the infection's area but typically consist of frequent urination, a burning sensation throughout urination, strong-smelling or cloudy pee, and pelvic discomfort. In a lot more extreme instances, specifically when the kidneys are entailed, signs might likewise include fever, chills, and flank pain.
Danger variables for developing UTIs consist of sexual activity, certain kinds of birth control, urinary system abnormalities, and a weakened immune system. Prompt treatment is necessary to prevent complications, including kidney damages, and generally entails anti-biotics customized to the details microorganisms entailed.
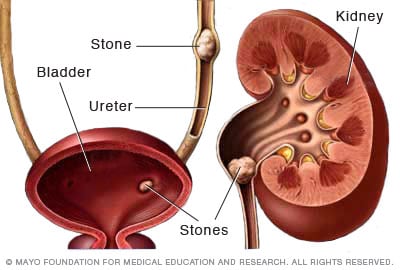
Therapy Choices for Kidney stones
If the stones are larger or trigger substantial pain, non-invasive treatments such as extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL) might be utilized. This technique uses acoustic waves to break the stones into smaller pieces that can be more conveniently gone through the urinary system.
In cases where stones are as well big for ESWL or if they block the urinary system, ureteroscopy may be suggested. This minimally intrusive treatment involves using a small scope to break or get rid of up the stones directly.
Treatment Choices for UTIs
How can doctor successfully deal with urinary system tract infections (UTIs)? The primary technique includes a comprehensive analysis of the client's symptoms and case history, adhered to by ideal diagnostic testing, such as urinalysis and pee society. These tests aid identify the original pathogens and determine their antibiotic vulnerability, leading targeted therapy.
First-line treatment usually includes antibiotics, with choices such as nitrofurantoin or trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, depending upon local resistance patterns. For uncomplicated instances, a brief program of anti-biotics (3-7 days) is typically enough. In persistent UTIs, suppliers may take into consideration different approaches or prophylactic prescription antibiotics, including way of life modifications to lower risk aspects.
For patients with difficult UTIs or those with underlying health and wellness issues, more hostile therapy might be needed, potentially including intravenous antibiotics and additional diagnostic imaging to analyze informative post for issues. Furthermore, client education and learning on hydration, hygiene techniques, and sign monitoring plays a crucial role in prevention and reappearance.
Comparing Results and Efficiency
Reviewing the results and performance of treatment choices for urinary system tract infections (UTIs) is important for enhancing individual treatment. The key therapy for uncomplicated UTIs generally entails antibiotic therapy, with alternatives such as fosfomycin, nitrofurantoin, and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole.
In comparison, treatment end results for kidney stones differ substantially based on stone place, size, and structure. Alternatives range from traditional monitoring, such as hydration and pain control, to interventional procedures like extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL) and ureteroscopy. While ESWL has a high success rate for smaller stones, issues can arise, requiring more treatments.
Inevitably, the performance of treatments for both problems depends upon precise medical diagnosis and customized approaches. While UTIs usually respond well to antibiotics, kidney stone administration might need a diverse strategy. Continuous analysis of therapy results is vital to improve patient experiences and minimize reoccurrence prices for both UTIs and kidney stones.
Verdict
In summary, therapy techniques for kidney stones and urinary Visit Your URL system tract infections vary considerably due to the distinctive nature of each problem. Non-invasive techniques such as extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy are ideal for smaller sized stones, whereas larger or obstructive stones may require ureteroscopy.
While UTIs are generally attended to with prescription antibiotics that offer fast relief, the technique to kidney stones can differ dramatically based on individual factors such as stone dimension and composition. Non-invasive methods like extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL) may be appropriate for smaller stones, yet larger navigate here or obstructive stones often need even more invasive strategies. The primary kinds of kidney stones include calcium oxalate, calcium phosphate, struvite, uric acid, and cystine stones, each with distinct biochemical origins.In comparison, therapy outcomes for kidney stones vary substantially based on stone make-up, size, and location. Non-invasive methods such as extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy are suitable for smaller sized stones, whereas bigger or obstructive stones may call for ureteroscopy.
Report this page